Open problems and innovations
Here, we list a few open problems and our solutions in the space of accessibility of biological data.
Accessibility of Genomic Visualization
There are several unique aspects about genomic visualization, such as the variety of visualization designs. These aspects make it even more difficult to make genomic visualization accessible.
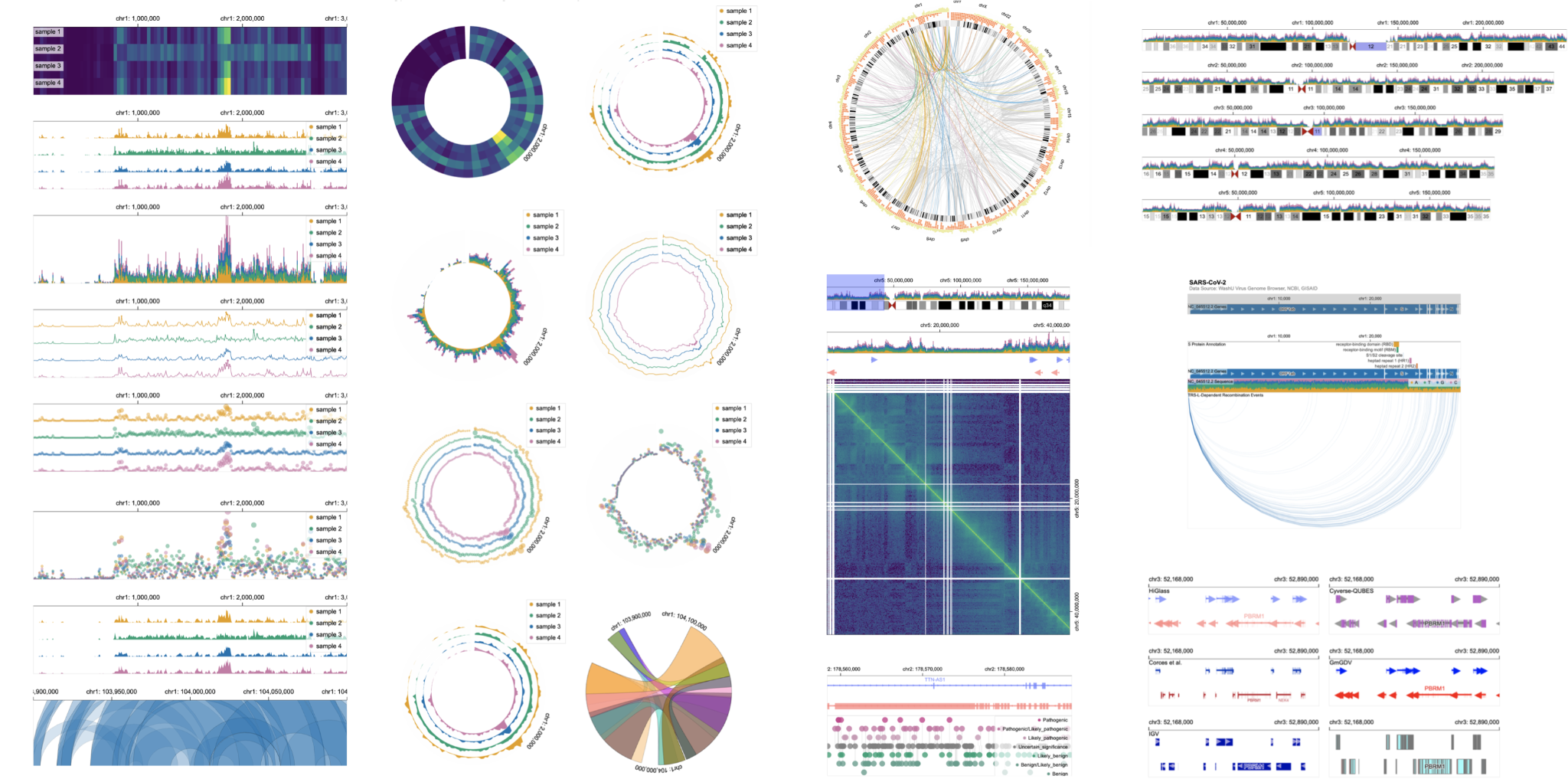
- Challenges
- Variety of visualization designs (e.g., Circos, Sequence Logos)
- Many visualizations at once (8.1 tracks on average)
- User interactions (e.g., zoom and pan)
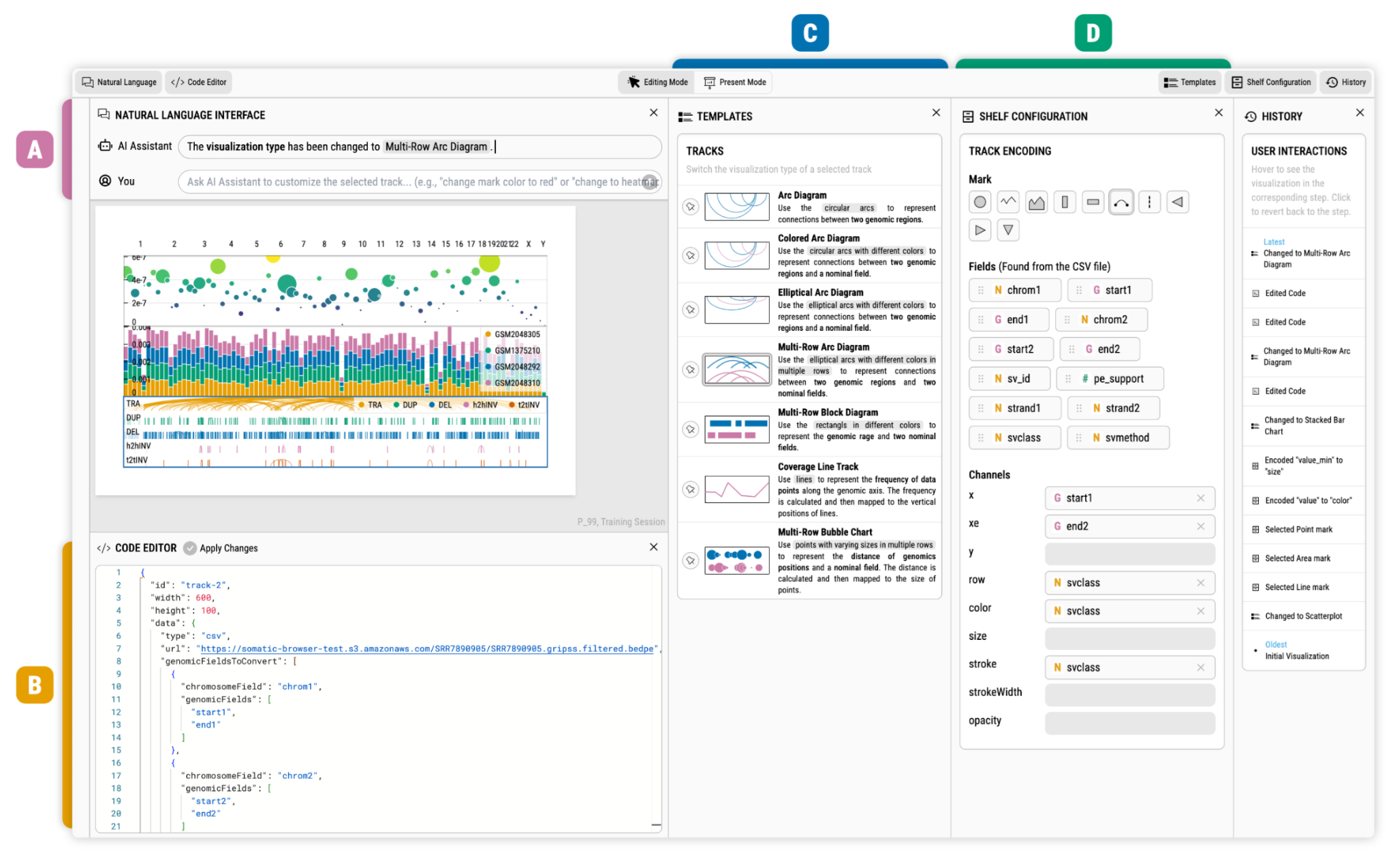
AltGosling (Demo, Paper)
- Automatic generation of text descriptions for accessible genomics data visualization
- AltGosling uses structured information in Gosling specifications in JSON to automatically create human-readable descriptions that describe the given visualization.


Blace (Paper)
- LLM-based Multimodal Visualization Authoring
- Through multimodal interactions, including chatbot interfaces, uesrs can more easily interactive with the system and build complex genomic data visualizations.
Accessibility of Data Portals
In our study, only 55.3% were successful for a screen reader to perform common tasks in data portals (inscidar.org).
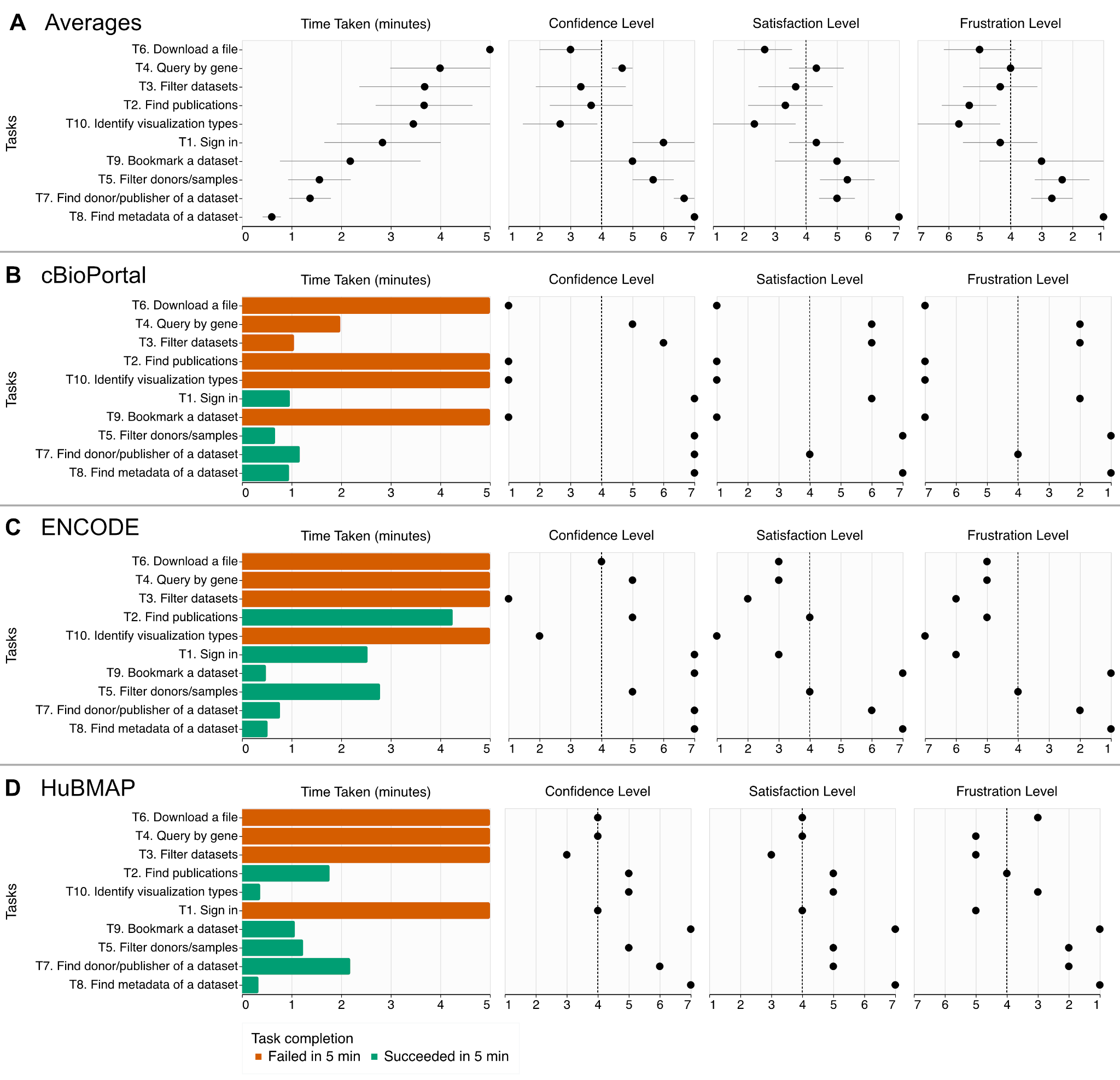
INSCIDAR Project
You can visit our project website (inscidar.org) to see our evaluation results and visualizations. We will run accessibility evaluation annually and release the results in this website.